Earliness is the key target character of current machine-picked cotton breeding, which has an important impact on improving the efficiency of machine-picking and realizing the whole-process mechanization of cotton planting. The node of the first fruiting branch (NFFB) is a reliable indicator to identify the earliness of cotton. It has good stability and is less affected by diseases and pests. Therefore, the discovery of NFFB-related regulatory genes will help to further understand the molecular regulatory mechanism of cotton earliness and promote the breeding of machine-picked cotton.
Recently, a research paper entitled “QTL mapping and BSA-seq map a major QTL for the node of the first fruiting branch in cotton” was published online by the cotton breeding team of the Institute of Cereal and Oil Crops in Frontiers in Plant Science.
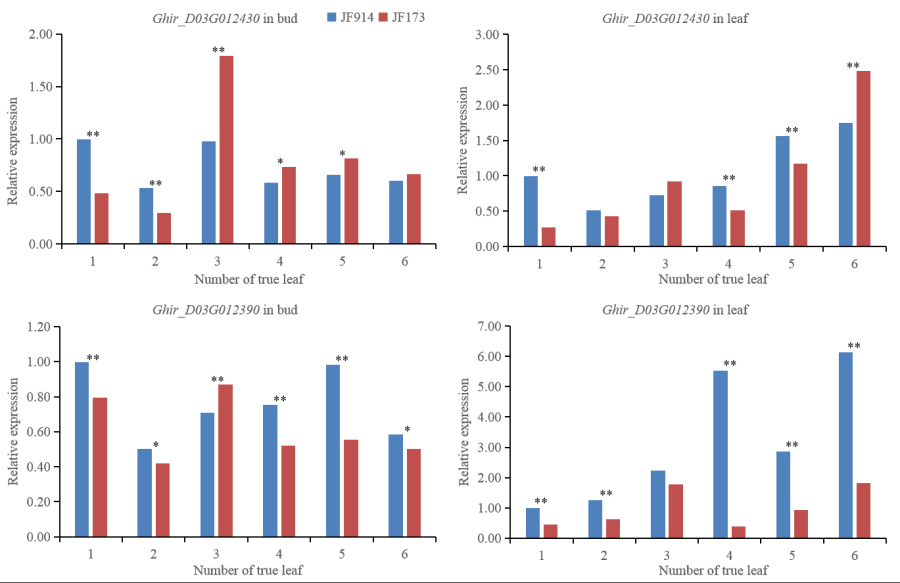
In this study, JF914, a medium-maturity national approved variety with 8-9 NFFB, was used as the maternal parent, and JF173, an early-maturity variety with 4-5 NFFB, was used as the paternal parent to construct a separate population. Combined with high-density SNP genetic map, 13 NFFB-related QTLs were located in F2, F3 and F4 populations, of which qNFFB-D3-1 had the best stability and the highest contribution rate, spanning about 24.7 Mb (17 130 008-41 839 226 bp). At the same time, a line with similar phenotype to JF914 and with 4-5 NFFB was selected from F4 population as the maternal parent, and backcrossed with JF914 to construct a BC1F2 population. Two NFFB-related regions on D3 chromosome were located by using BSA-seq and covered about 92.4 Kb (41 779 195-41 836 120 bp and 41 836 768-41 872 287 bp). This 92.4 Kb region overlapped with qNFFB-D3-1 and contained 8 annotated genes. By qRT-PCR, Ghir_D03G012430 was expressed at a lower level at 1- and 2-leaf stages and increased sharply to a higher level at 3- to 6-leaf stages in the buds of JF173 than that of JF914. Ghir_D03G012390 reached the highest expression level in the buds of JF173 and JF914 at 3- and 5-leaf stages, respectively. As reported, Ghir_D03G012430 functions in cell asymmetric division, development and aging, and D3 chromosome is closely related to cotton earliness. Since the NFFB of JF173 was formed earlier than JF914, it was speculated that Ghir_D03G012430 and Ghir_D03G012390 may participate in regulating the formation of NFFB and affect cotton earliness.
Doctor JIA Xiaoyun from the cotton breeding team of Institute of Cereal and Oil Crops is the first author. Researcher LI Miao is the corresponding author.
Address of publication:
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2023.1113059/full
(Source from www.hebnky.com)